Dr. Duff's Take on Rosacea
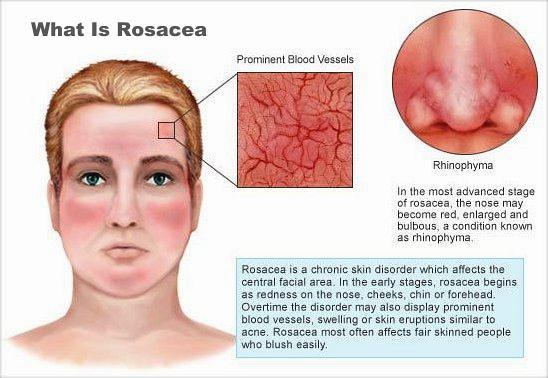
- Redness or flushing
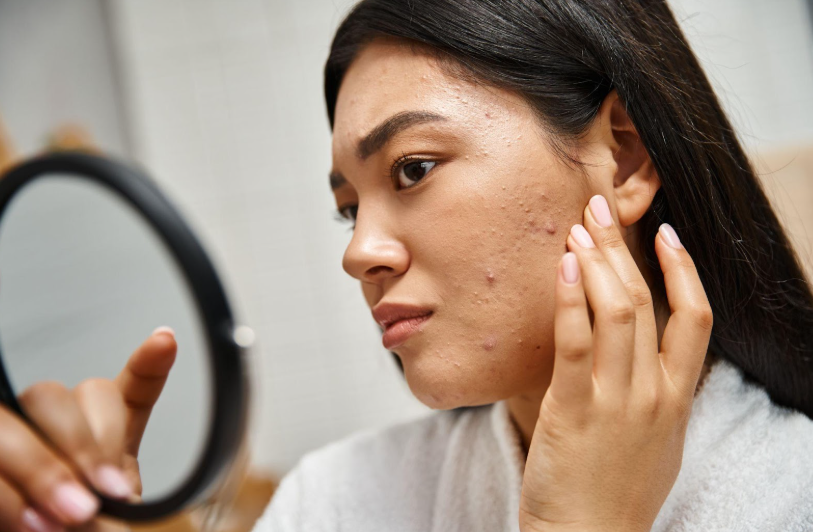
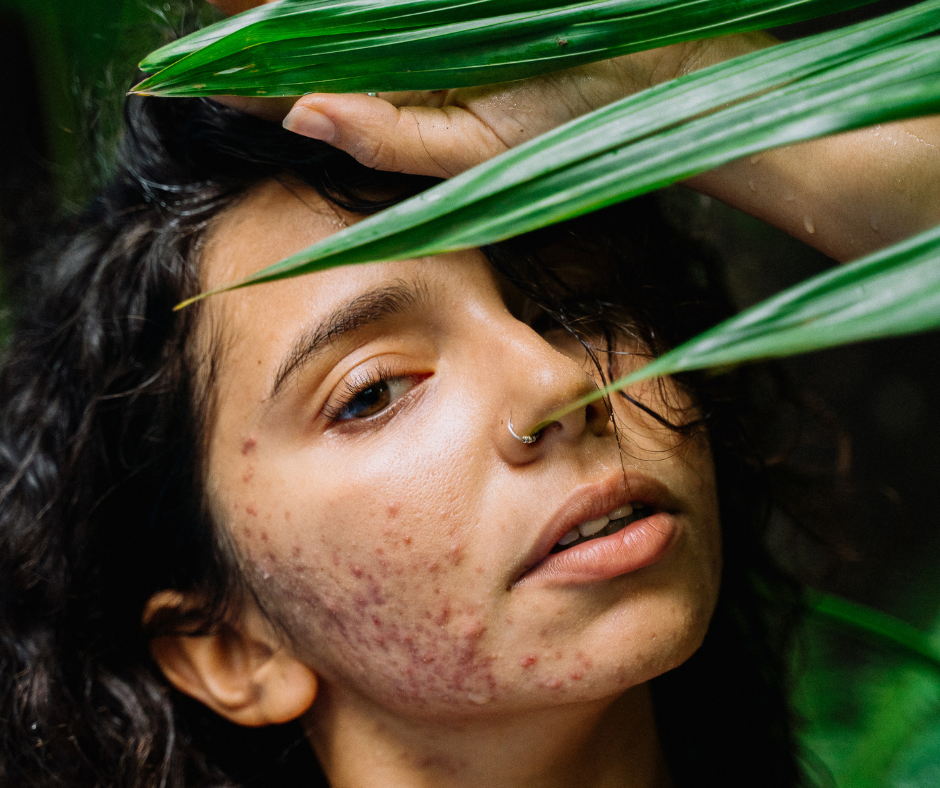
- Papules or pustules (acne)
- Burning, stinging
- Thickening of the skin (especially the nose)
- Red, dry, irritated (gritty feeling) in the eyes
- Periodic flares (ups and downs)
- Erythematotelangiectatic: Redness, easy blushing, dilated visible blood vessel
- Papulopustular: Redness with pustules (acne like)
- Phymatous: rhinophyma (thickening of the skin usually the nose)
- Ocular: eyes are red and feel irritated, dry and gritty
- Family history: it runs in families and is more common in fair skinned individuals
- Demodex folliculorum (mite that lives on human skin which usually does not cause any problems but in people with rosacea there is an increase number of these mites in the skin. No one knows if the mites cause rosacea or if rosacea causes an over production of mites
- H pylori which is a bacteria in the gut can stimulate bradykinins (a protein that causes blood vessels to dilate). Although H pylori is common in people with rosacea there are people who have H pylori and do not have rosacea.
- Stress and anxiety
- Hot liquids
- Caffeine
- Alcohol
- Spicy foods
- Exercise
- Temperature extremes (Hot or cold weather)
- Humidity
- Wind
- Hot bath or shower
- Topical and/or oral antibiotics
- Topical medications to target the demodex mite in the skin
- Gentle cleansers
- Lasers
- Newer topical medications that can temporarily control the redness
- Avoiding known triggers