Everything You Need to Know About Genital Herpes
Everything You Need to Know About Genital Herpes

One of the most prevalent STIs in the world is genital herpes. Despite its prevalence, there is still a great deal of misinformation surrounding the virus. If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with genital herpes, understanding the condition can help with management and prevention.
Though lifelong, the infection can be managed with treatments that reduce symptoms and transmission. Here's everything you should know about genital herpes.
What Is Genital Herpes?
The herpes simplex virus (HSV) causes genital herpes and is classified into two types: HSV-1 and HSV-2. While HSV-1 is commonly associated with cold sores around the mouth, it can also cause genital infections through oral-genital contact. HSV-2 is more commonly linked to genital herpes and spreads primarily through vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
The virus enters the body through mucous membranes or small skin abrasions. Once inside, it remains in nerve cells and can reactivate periodically, causing recurrent outbreaks. Genital herpes is highly contagious, even when no visible sores or symptoms are present.
How Common Is Genital Herpes?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the infection affects a significant portion of the global population:
- Over 500 million people worldwide are living with genital herpes caused by HSV-2.
- Approximately 3.8 billion people under age 50 have HSV-1, which is commonly associated with oral herpes but can also lead to genital infections through oral-genital contact.
- Many individuals remain asymptomatic or experience mild, unrecognized symptoms, leading to unintentional transmission.
Why is this important?
If you’ve had unprotected sexual contact, a new partner, or any symptoms—no matter how mild—getting tested is crucial. Early diagnosis allows for effective management, reduces outbreaks, and lowers the risk of passing the virus to others. Understanding your risk and seeking medical advice when needed can help control the spread of herpes and promote safer sexual health.
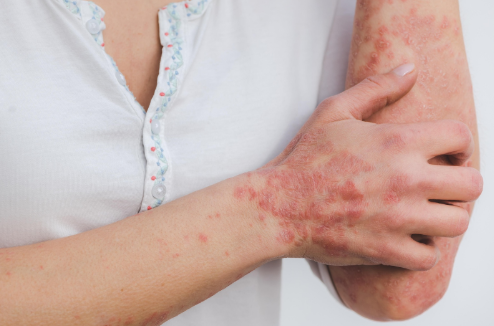
What are the Symptoms of Genital Herpes?
Not everyone with genital herpes experiences symptoms, and some may carry the virus without ever having an outbreak. However, when symptoms do occur, they can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, depending on the individual's immune response and whether it is a first-time outbreak or a recurrence.
Primary Outbreak Symptoms
The first outbreak, known as the primary episode, typically occurs 2 to 12 days after exposure and is often the most severe. Symptoms may last for 2 to 4 weeks and include:
- Clusters of painful blisters or open sores on the genitals, inner thighs, buttocks, or anus, which may break open and ooze before scabbing over.
- Itching, tingling, or burning sensations in the affected area, often serving as a warning sign before blisters appear.
- Flu-like symptoms, including fever, chills, swollen lymph nodes (especially in the groin), headaches, and muscle aches.
- Painful urination, particularly if sores develop near the urethra, makes it difficult to pass urine.
- General discomfort and fatigue as the body fights off the initial infection.
Women may also experience vaginal discharge and pain during intercourse, while men might notice sores on the scrotum or penis. The first outbreak can be physically and emotionally challenging, but symptoms gradually subside as the body builds an immune response.
Recurrent Outbreaks
After the initial infection, the herpes virus remains dormant in nerve cells and can reactivate at any time. While recurrences are usually less severe and shorter in duration—often lasting 5 to 10 days—they can still cause discomfort. Common signs of a recurring outbreak include:
- A Warning Sensation (Prodrome): Many individuals notice tingling, burning, itching, or mild discomfort in the affected area one to two days before blisters appear. Some may also feel an ache or tightness in the lower back, buttocks, or legs, which signals an impending outbreak.
- Smaller Clusters of Sores: Unlike the widespread lesions of the primary outbreak, recurrent sores are typically fewer in number, smaller in size, and heal more quickly. They may still be painful but are generally less inflamed than those in the first outbreak.
- Mild Flu-like Symptoms: Some people experience low-grade fever, mild fatigue, headache, or muscle aches, though these symptoms are typically much less intense than during the primary infection.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: The lymph nodes in the groin may become slightly swollen during a recurrent outbreak, though not as prominently as in a first episode.
- Painful Urination: If sores develop near the urethra, urination can cause burning or stinging, but this is usually milder than in a primary outbreak.
What are the Factors That May Trigger a Recurrence?
While herpes outbreaks cannot always be completely prevented, identifying personal triggers and taking proactive steps to reduce exposure to them can help in managing the condition effectively. While triggers vary from person to person, understanding what may prompt an outbreak can help in managing the condition and reducing frequency.
Emotional or Physical Stress
High levels of stress—whether due to work pressure, major life changes, relationship difficulties, or emotional distress—can weaken the immune system, making it easier for the virus to reactivate. Practicing stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing, or regular exercise, can help reduce outbreak frequency.
Weakened Immune System
Any condition that compromises the immune system, such as colds, flu, chronic illnesses, or immune-suppressing medications, can trigger an outbreak. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, and adequate rest can help strengthen immune defenses.
Hormonal Fluctuations
Changes in hormone levels, particularly during menstruation, pregnancy, or hormone therapy, can influence outbreaks. Some individuals notice a pattern of recurrences right before or during their menstrual cycle, making it helpful to track symptoms and adjust self-care accordingly.
Lack of Sleep or Chronic Fatigue
Inadequate rest and prolonged exhaustion put stress on the body, making it harder for the immune system to suppress viral activity. Prioritizing consistent sleep schedules and proper relaxation can help minimize outbreaks.
Friction from Sexual Activity or Tight Clothing
Prolonged friction, irritation, or excessive heat in the genital area—whether from sexual activity, tight-fitting underwear or synthetic fabrics—can aggravate the skin and lead to a recurrence. Opting for breathable cotton underwear and using lubricants during intimacy may help reduce irritation.
Excessive Sun Exposure or Extreme Weather Conditions
Prolonged UV exposure, extreme heat, or cold weather can stress the body and weaken immunity, increasing the risk of an outbreak. If sun exposure is a trigger, using sunscreen and staying hydrated can help minimize the risk.
Poor Diet and Dehydration
Nutrient deficiencies, excessive alcohol intake, processed foods, or dehydration can weaken the body’s ability to keep the virus dormant. A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and hydration can help maintain overall immune health and reduce the likelihood of recurrences.
How Is Genital Herpes Diagnosed?
If you suspect you have genital herpes, consulting a medical professional is the best way to confirm the diagnosis. They include:
- Visual Examination: A doctor may diagnose herpes based on visible sores.
- Viral Culture or PCR Test: A sample from a sore is tested for the presence of HSV.
- Blood Test: Detects antibodies against HSV to determine past or current infection.
Early diagnosis is crucial for managing symptoms and reducing transmission risks. If you’re sexually active, regular STI screenings can help detect infections even if you have no symptoms.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for genital herpes, effective treatments help control symptoms, reduce outbreaks, and lower transmission risks.
- Antiviral Medications: Acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir speed up healing, shorten outbreaks, and decrease viral shedding. They work best when taken at the first sign of symptoms or as a daily preventive measure for frequent outbreaks. These medications also help reduce asymptomatic viral shedding, lowering the risk of transmission.
- Suppressive Therapy: For those with frequent or severe outbreaks, daily antiviral medication reduces recurrence by up to 80% and lowers the risk of passing the virus to a partner. This approach is often recommended for individuals in long-term relationships or those with weakened immune systems.
- Episodic Therapy: This approach involves taking antiviral medication only when symptoms appear to shorten the duration and reduce the severity of an outbreak. It is most effective when started at the first sign of symptoms, such as tingling or itching, and can help speed up healing while minimizing discomfort.
- Pain Relief: Ibuprofen and acetaminophen help relieve discomfort, while warm baths with Epsom salts can soothe irritation. Lidocaine or aloe-based creams may provide temporary relief from itching and burning. Wearing loose, breathable clothing can also prevent further irritation.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Managing stress through exercise, meditation, or therapy, maintaining good sleep habits, staying hydrated, and eating a nutrient-rich diet help strengthen the immune system and reduce outbreaks. Avoiding excessive sun exposure, alcohol, and smoking may also lower recurrence rates.
Psychological and Social Impact
Seeking mental health support, joining support groups, or speaking with a therapist can help individuals manage these emotional challenges. Honest communication with partners also plays a key role in maintaining healthy relationships.
How We Support You
Our team offers confidential counseling to address emotional concerns, reduce stigma, and build confidence in relationships. We also provide partner communication coaching, helping you have open, informed conversations about herpes with loved ones.
Additionally, our tailored wellness programs focus on immune-boosting strategies and preventive care, ensuring you have the tools to manage outbreaks effectively and live confidently.
Whether you are experiencing a recurring infection or dealing with a stubborn case, we, at
Pine Belt Dermatology, can help you restore your skin's health seamlessly. Visit
our services page to learn more about our treatments for your skin problems and a tailored treatment plan from our experts.
Book your consultation today!